Life Science and Pharmaceutics
The Raman spectrum is unique for each chemical composition and provides qualitative and quantitative information of the material. From measurements in liquids to solid samples or soft tissues in life science are particularly well-suited for the technique. It is an efficient and reliable analytical tool in pharmaceutical R & D and production of drug delivery systems.
Materials science
Analysis in material science offers detailed knowledge of sample surface morphology and chemical composition. Raman imaging provides chemical data, while AFM detects topography, structure, and
physical properties like stiffness, adhesion, and viscosity. Versatile instrument combinations in a single unit can include confocal Raman imaging, Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), Nearfield-Microscopy (SNOM) and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM).
Nano-Carbon & 2D Materials
2D materials like carbon nanotubes, graphene, and TMDs offer huge potential for transistors, sensors, and optoelectronics. Flexible methods like Raman analysis help drive faster research and development in this field.
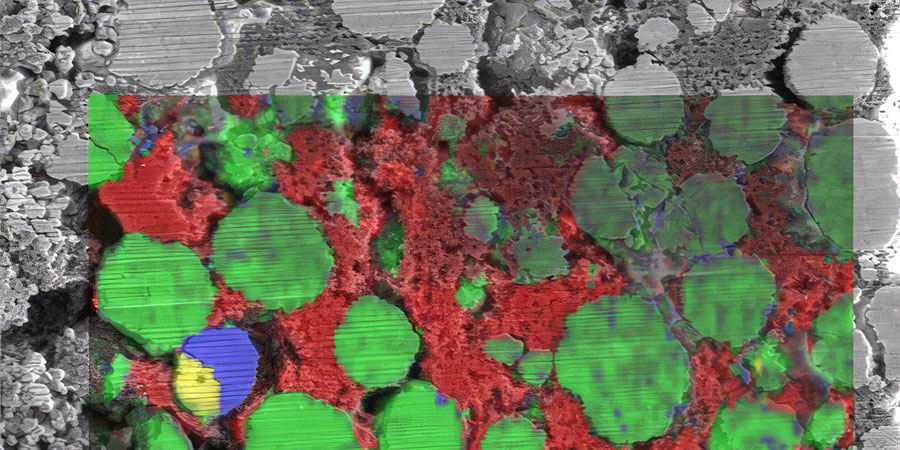
Energy Storage & Batteries
Battery research focuses on improving charging speed, energy density, and lifespan. Raman imaging reveals the distribution and crystallinity of materials in batteries and fuel cells, and can be combined with other imaging techniques for detailed surface analysis.
Cell Biology
The non-invasive and label-free nature of confocal Raman imaging microscopy makes it a powerful technique for cell biology applications to study cellular processes such as lipid organization, metabolism, infection and drug uptake.
The flexible and multimodal imaging platform ranging from classical Epi-fluorescence up to multi-photon and higher harmonic microscopy is ideal for unlimited fields of life science.



